Samsung outs ISOCELL phone camera sensor, touts superior low-light abilities
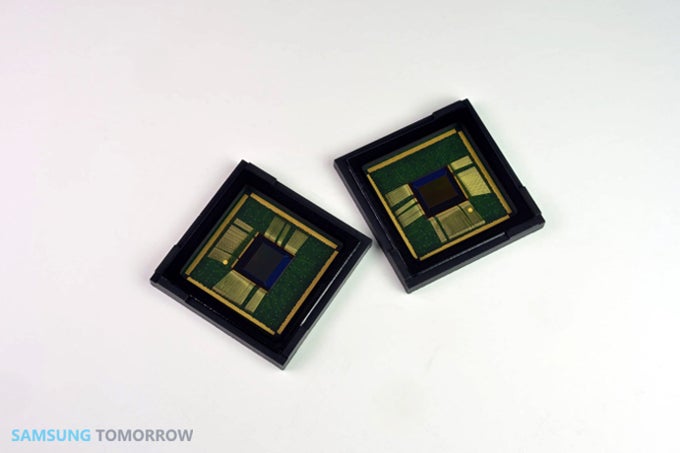

With ISOCELL, each individual pixel is isolated, and can grab more photons from the light that pours into the sensor, compared to the diffusion that goes on with the BSI tech. Long story short, this means we should expect much better exposed and blur-free photos in low light, which is the hardest scenario for any camera to make decent photos in.
In fact, Samsung has even calculated that phones and tablets using ISOCELL modules will have 30% better color accuracy just from the sensor itself, as well as 30% better dynamic range capture. Not only that, but the tech allows for much lower modules, which means they can be fit into ever slimmer handsets and slates. As you can see in Samsung's comparison image below, the tech really sports more correct dynamic range and exposure measurements, as well as better color representation than BSI.

Samsung's first sensor to adopt ISOCELL, the S5K4H5YB, is an 8 MP unit with 1.12 micron ISOCELL pixels and a 1/4" format. It is already sampling to customers, and mass production is starting in Q4, so we'll be able to see the results very soon. If some form of this goes into the Galaxy S5, paired with optical image stabilization, and the rumors about a metal body and 64-bit processor pan out, next year's Samsung flagship might be the one to get.
SEOUL, South Korea, Sep 23, 2013 (BUSINESS WIRE) — Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., a world leader in advanced semiconductor solutions, today announced its new advanced pixel technology for CMOS image sensors, ISOCELL. This new technology substantially increases light sensitivity and effectively controls the absorption of electrons, resulting in higher color fidelity even in poor lighting conditions. ISOCELL improves the image quality and enhances the user experience of premium smartphones and tablets that integrate sensors with this exciting new technology.
“Through advances in pixel and process technology, smartphone and tablet cameras have made it easier than ever for consumers to capture and share beautiful, clear images with the world,” said Taehoon Kim, vice president of System LSI marketing, Samsung Electronics. “ISOCELL technology is yet another innovation that significantly raises the bar in image quality, and demonstrates Samsung’s technology leadership in image sensors for mobile devices.”
The quality of an image sensor is determined by the amount of light that is accurately captured by the individual pixels within the sensor array. With the market pressure to increase camera resolution and image quality, without growing the camera size, the pixels have had to shrink, while improving their performance at the same time – a challenging task.
To meet this challenge, previous sensor technology developments focused on improving the light absorption of each pixel, and have progressed pixel technology from FSI (Front Side Illumination) to BSI (Back Side Illumination) which places photodiode at the top to maximize photoelectric efficiency. While being very effective at the time, this BSI technology also faced limitations in improving image quality as pixel sizes continued to decrease.
Building on these past advances and continuing the push toward higher quality image sensors for mobile devices, Samsung has developed ISOCELL the next generation of pixel technology, which is patent pending. ISOCELL technology forms a physical barrier between neighboring pixels – isolating the pixel. This isolation enables more photons to be collected from the micro-lens and absorbed into the correct pixel’s photodiode minimizing undesired electrical crosstalk between pixels and allowing expanded full well capacity (FWC).
Compared to conventional BSI pixels, the ISOCELL pixels decrease the crosstalk by approximately 30 percent which results in higher color fidelity to reproduce the original color with sharpness and richness, and increase the full well capacity (FWC) by 30 percent which leads to greater dynamic range.
Additionally, an imager designed with ISOCELL can feature a 20 percent wider chief ray angle (CRA), reducing the height of the camera module. This makes it suitable for slim and small form factor mobile devices with challenging low z-height requirements.
As the first Samsung image sensor to adopt this new technology, the S5K4H5YB 8Megapixel imager utilizes a 1.12um ISOCELL pixel and has a 1/4inch optical format. The S5K4H5YB is currently sampling to customers with mass production scheduled for Q4 2013.
According to market research firm Techno System Research, in 2014, approximately 66 percent of smartphones will feature image sensors with 8Mp or higher resolution.
“Through advances in pixel and process technology, smartphone and tablet cameras have made it easier than ever for consumers to capture and share beautiful, clear images with the world,” said Taehoon Kim, vice president of System LSI marketing, Samsung Electronics. “ISOCELL technology is yet another innovation that significantly raises the bar in image quality, and demonstrates Samsung’s technology leadership in image sensors for mobile devices.”
The quality of an image sensor is determined by the amount of light that is accurately captured by the individual pixels within the sensor array. With the market pressure to increase camera resolution and image quality, without growing the camera size, the pixels have had to shrink, while improving their performance at the same time – a challenging task.
To meet this challenge, previous sensor technology developments focused on improving the light absorption of each pixel, and have progressed pixel technology from FSI (Front Side Illumination) to BSI (Back Side Illumination) which places photodiode at the top to maximize photoelectric efficiency. While being very effective at the time, this BSI technology also faced limitations in improving image quality as pixel sizes continued to decrease.
Building on these past advances and continuing the push toward higher quality image sensors for mobile devices, Samsung has developed ISOCELL the next generation of pixel technology, which is patent pending. ISOCELL technology forms a physical barrier between neighboring pixels – isolating the pixel. This isolation enables more photons to be collected from the micro-lens and absorbed into the correct pixel’s photodiode minimizing undesired electrical crosstalk between pixels and allowing expanded full well capacity (FWC).
Compared to conventional BSI pixels, the ISOCELL pixels decrease the crosstalk by approximately 30 percent which results in higher color fidelity to reproduce the original color with sharpness and richness, and increase the full well capacity (FWC) by 30 percent which leads to greater dynamic range.
Additionally, an imager designed with ISOCELL can feature a 20 percent wider chief ray angle (CRA), reducing the height of the camera module. This makes it suitable for slim and small form factor mobile devices with challenging low z-height requirements.
As the first Samsung image sensor to adopt this new technology, the S5K4H5YB 8Megapixel imager utilizes a 1.12um ISOCELL pixel and has a 1/4inch optical format. The S5K4H5YB is currently sampling to customers with mass production scheduled for Q4 2013.
According to market research firm Techno System Research, in 2014, approximately 66 percent of smartphones will feature image sensors with 8Mp or higher resolution.
source: Samsung
Follow us on Google News










![A new Android bug is making it impossible to install new apps. Are you affected? [UPDATE]](https://m-cdn.phonearena.com/images/article/176703-wide-two_350/A-new-Android-bug-is-making-it-impossible-to-install-new-apps.-Are-you-affected-UPDATE.webp)
Things that are NOT allowed:
To help keep our community safe and free from spam, we apply temporary limits to newly created accounts: