Apple Glass users' eyes can determine how engaged they are to the content they're viewing

Apple has filed a patent application for a system that can gauge how interested an Apple Glass wearer is in the content being displayed on the headset and can adjust the brightness of the display and even change the content. This is done by measuring whether the user's eyes are dilated or constricted while viewing certain content. The point of the technology in the patent application titled "Utilization Luminance Changes to Determine User Characteristics" is to "identify a state of a user (e.g., attentive, distracted, mind wandering, etc.) based on the user's physiological (e.g., pupillary) response to luminance change events in which a portion or all of the content quickly becomes brighter or dimmer."
Apple Glass could measure a user's eyes to determine if he is paying attention to the content on the displays
In one example, Apple says "if the luminance of the content increases while the user is attentive and engaged, the pupillary response may be slower and smaller in magnitude" compared to when they're tired. With this in mind, the headset can examine the user's eyes to determine whether he or she is paying attention to the content, or is bored and distracted. Apple could also use the response of the user's eyes to suggest that the user take a break. And the technology can help Apple make changes to the display's brightness to make sure that the user is comfortable viewing the device's content.
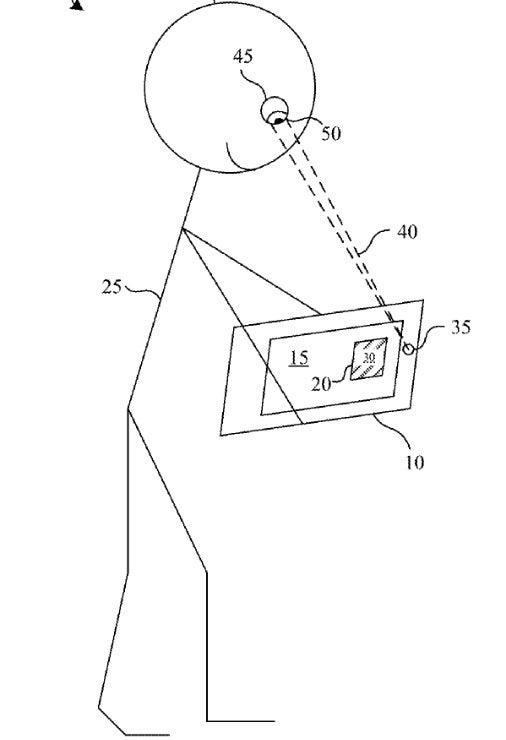
Illustration from Apple's patent application
In the filing with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, Apple states "In some implementations, a device having a processor, a display, and a sensor implements a method. The method identifies a luminance change event associated with content on the display. The luminance change event may be a relatively quick change to brighter or dimmer content viewed by the user. The luminance change event may occur naturally as the user scans the content or be embedded intentionally in the content for purposes of triggering a response that can be used to assess state. The method uses the sensor to obtain a physiological response (e.g., a pupillary dilation or constriction) of a user perceiving the luminance change event associated with the content on the display. In some implementations, for example, an inward facing camera on a head-mounted device (HMD) captures images of the user's eye and a pupil diameter/radius is determined via a computer vision technique."
By determining the user's response to certain content, creators will be able to deliver "tailored" user experiences that users will more likely enjoy based on physiological responses in users viewing the content." In the filing, Apple says, "In some implementations, a device having a processor, a display, and a sensor implements a method. The method identifies a luminance change event associated with content on the display. The luminance change event may be a relatively quick change to brighter or dimmer content viewed by the user. The luminance change event may occur naturally as the user scans the content or be embedded intentionally in the content for purposes of triggering a response that can be used to assess state. The method uses the sensor to obtain a physiological response (e.g., a pupillary dilation or constriction) of a user perceiving the luminance change event associated with the content on the display. In some implementations, for example, an inward facing camera on a head-mounted device (HMD) captures images of the user's eye and a pupil diameter/radius is determined via a computer vision technique. The method assesses the state of the user based on the pupillary response. The state may be determined based on magnitude and/or dynamics of the pupillary response. In some implementations, the pupillary response is compared with the user's own prior responses to determine the user's current state. In some implementations, the pupillary response is assessed based on pupillary responses of multiple users to various types of content, e.g., comparing the user's current pupillary response with a typical or average user response to a similar luminance change event. In some implementations, the state is determined using statistical or machine learning-based classification techniques."
In a second patent application found by AppleInsider titled "Electronic Device Having Display With Internal Light Reflection Suppression," Apple looks at how light is reflected in a headset with the goal of minimizing discomfort to those wearing an Apple headset. Displays used in headsets with a high pixel density and surface imperfections could scatter trapped light outwardly reducing the contrast of the display. Apple's plan is to use antireflection layers to prevent this from happening.
Apple is expected to release an expensive mixed display headset next year followed in 2023 by the release of the AR powered Apple Glass.
Follow us on Google News











Things that are NOT allowed:
To help keep our community safe and free from spam, we apply temporary limits to newly created accounts: