Here's how Huawei plans on beating out Samsung to become number one
Thanks to its inclusion in the U.S. Commerce Department's Entity List, Huawei is banned from accessing its U.S. supply chain. As a result, it is unable to obtain a license to use Google Mobile Services on its phones. That means that Huawei's phones do not have Google's ecosystem and can't run Google's apps including the Play Store, Search, Maps, Gmail, Drive, and others. This isn't a big deal in China where most of Google's apps are banned anyway, but it certainly affects sales of Huawei's phones outside of China.
Overall, Huawei still managed to increase smartphone shipments by 35 million last year to 240 million units. That put the company in second place ahead of Apple but left it trailing Samsung for the crown. Huawei planned on finishing the year on top but nearly a year ago the U.S. announced that it had put Huawei on the Entity List for security purposes. But the company believes that it has a plan to attract more global buyers and take the smartphone crown from Samsung.
Differentiating itself from Google, Huawei says it is not a data company
Huawei has had to load its latest phones with an open-source version of Android containing its AppGallery app storefront. The latter is the third-largest distributor of apps in the world. AppGallery launched in China in 2011 and the international version was released in 2018. Huawei thinks that the key to surpassing Samsung is to make the AppGallery more secure and consumer friendly than the Google Play Store. Huawei is hitting Google where it is most vulnerable by making the AppGallery extremely secure. It plans on doing this by verifying that all developers are exactly who they say they are. Real names will be required and Huawei will check them out.
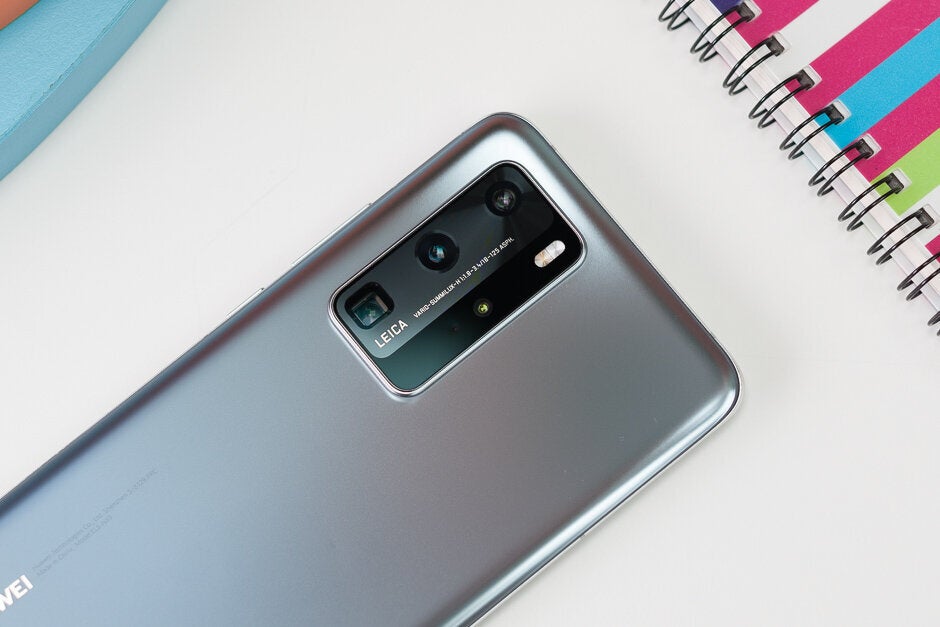

Huawei's current flagship phone, the P40 Pro
In addition, Huawei says that it will do better than Google in discovering apps loaded with malware. Over the last few years, we have passed along several stories about malware-loaded Android apps that forced Android users to pay for premium text services, slowed down their phone and drained the batteries by running ads in the background, and more. Huawei believes that it can do a better job vetting new apps for the AppGallery. And Huawei says that it won't send any data to servers in China which is exactly what it is always been accused of doing and is exactly what Xiaomi did.
And Huawei notes, with a little jab directed at Google, that it is not a data company. In other words, it isn't looking for the AppGallery to generate location data and other personal information that could be used by advertisers
Huawei still remains in a tough spot. The Trump administration has already drafted a change to the Direct Product Rule. This is the rule that allows the U.S. to control the export of products made in a foreign country if they contain 25% or more U.S. content by value. The U.S. is considering dropping that threshold to 10%; at that level, the U.S. could block a shipment of chips made by TSMC for Huawei. That would include the 5nm Kirin 1012 5G SoC which is expected to power the Mate 40 line later this year.
In China, where Huawei was treated kindly last year by consumers who considered the firm to be the victim of a schoolhouse bully, the company still had a huge market share (39%) during the first quarter. But a resurgent Apple could be a long-term worry. The company had the top-selling phone in China during the first quarter in the iPhone 11; in fact, the phone has topped the Chinese smartphone charts for seven consecutive months. And Huawei and Apple were the only phone manufacturers to post year-over-year market share gains in China during the three months from January through March. During the quarter Huawei's 39% slice of the Chinese smartphone pie was up from the 29% share it had a year earlier. Apple's share increased to 10% from last year's 8%.













Things that are NOT allowed: